Understanding the Modern Filament Bulb
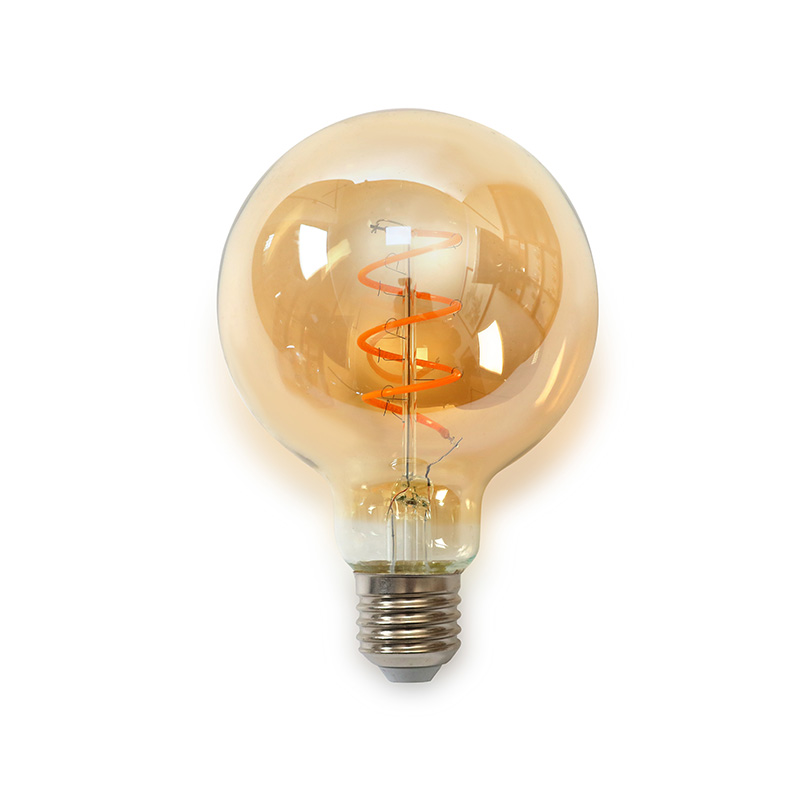
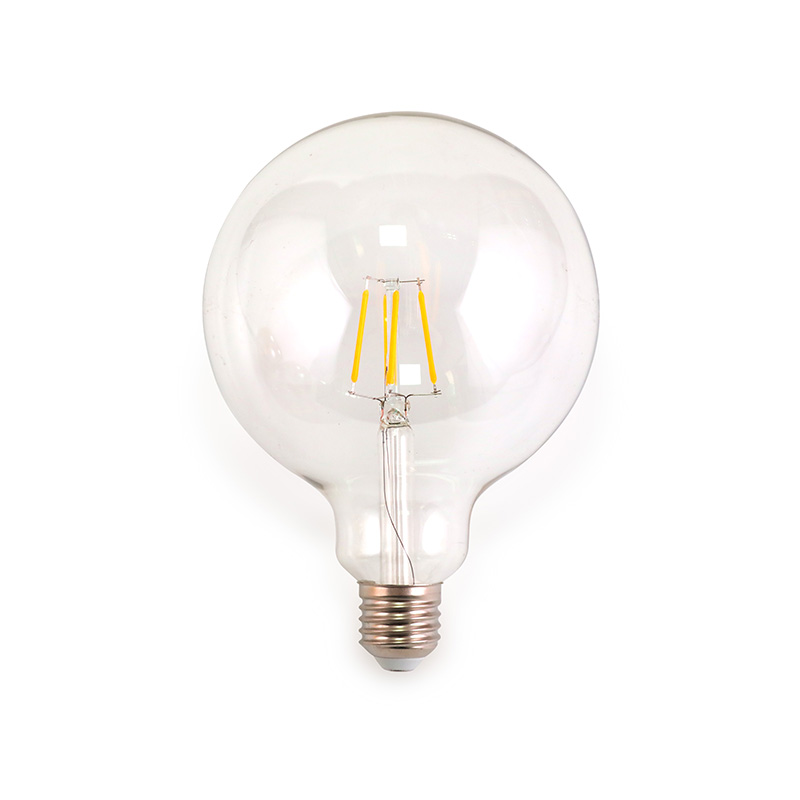
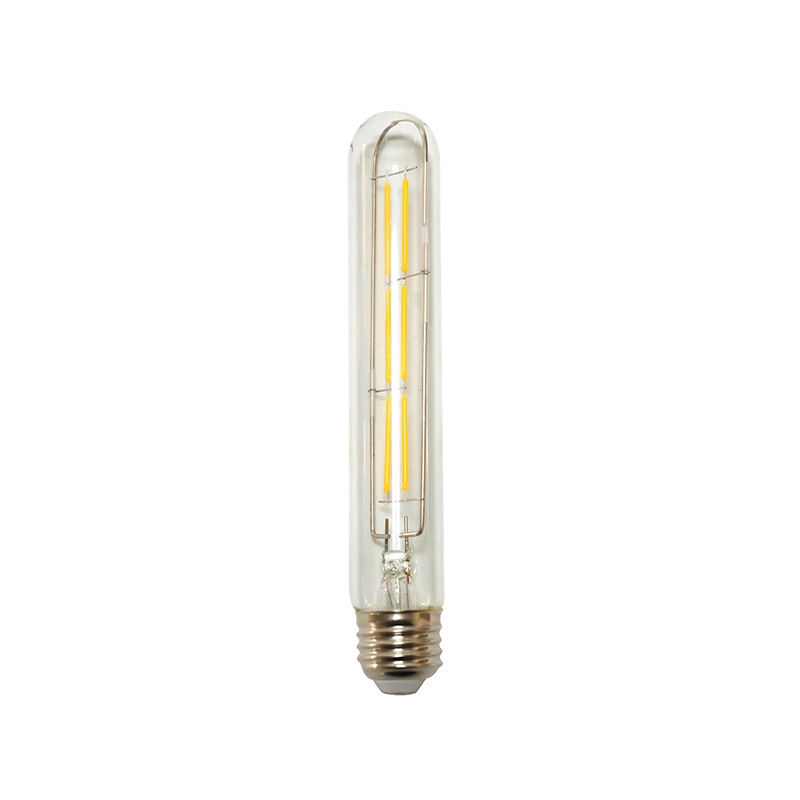
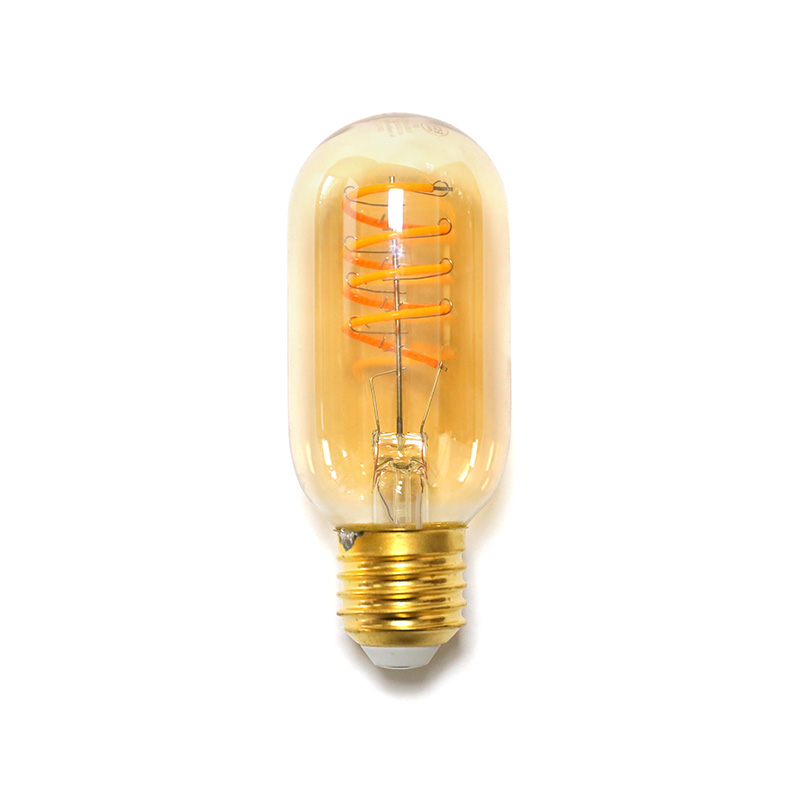
Home Filament Light Bulbs, often called Edison or vintage bulbs, are not the energy-guzzling incandescents of the past. Modern versions use advanced materials like carbon or improved tungsten filaments within LED or halogen technology. Their primary intent is aesthetic, designed to showcase the beautiful, intricate glow of the filament itself. They create a warm, inviting atmosphere ranging from soft amber to a bright, clear light, directly addressing the desire for decorative lighting that adds character to a space. Unlike vague "decor" lighting, these bulbs are a specific design element, often serving as the focal point of a fixture.
Selecting the Right Filament Bulb for Your Space
Choosing a filament bulb goes beyond wattage. You must consider several specific factors to achieve the desired look and function. The bulb's shape, filament pattern, and light temperature are crucial.
Key Selection Criteria
Focus on these concrete specifications when shopping:
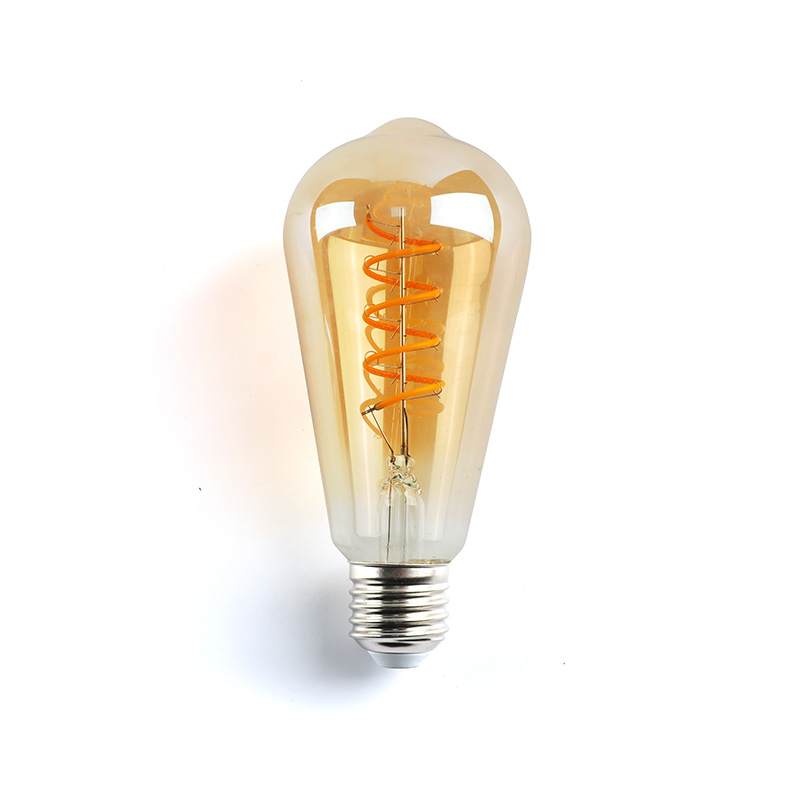
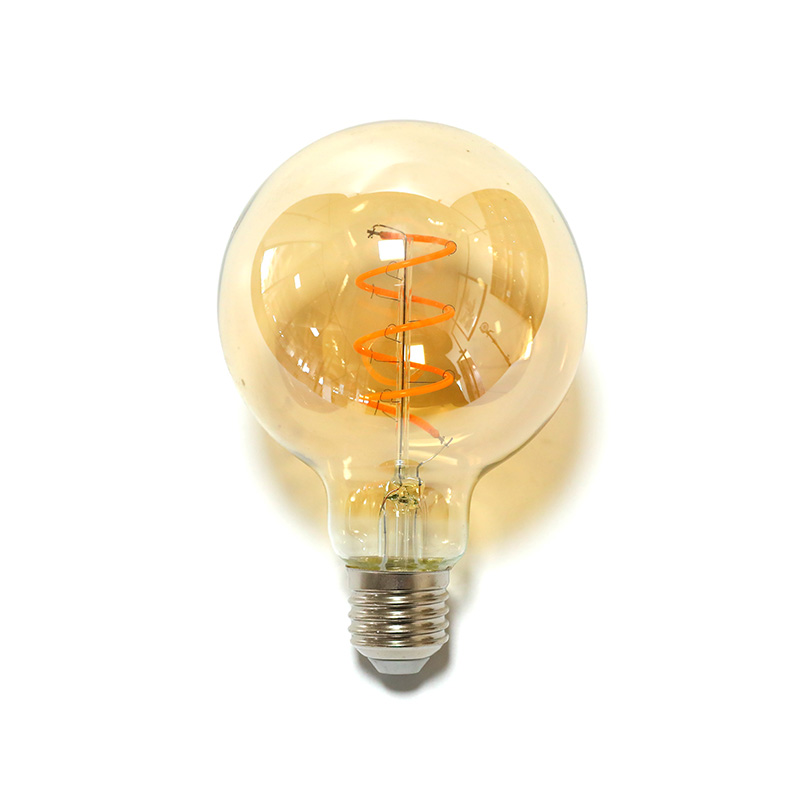
- Filament Style: Choose from squirrel cage, spiderweb, horseshoe, or linear designs. Each casts a unique shadow and glow pattern.
- Color Temperature: Measured in Kelvins (K). For that classic warm glow, look for 2200K (very amber) to 2700K (warm white). "Warm white" LEDs around 2700K mimic traditional incandescents.
- Lumens, Not Watts: Wattage indicates energy use. For brightness, check lumens (lm). A 400-800 lm bulb is good for ambient lighting in a pendant or table lamp.
- Base Type: Ensure compatibility. Common bases are E26 (standard US), E27 (standard EU), and E12 (candelabra).
- Dimmability: Not all are dimmable. If you need dimming, verify the bulb is explicitly labeled as dimmable and check compatibility with your dimmer switch.
Practical Applications and Placement
Filament bulbs excel in specific, exposed-bulb fixtures where their design can be appreciated. Their use is purposeful, not general.
- Pendant Lights & Chandeliers: Over dining tables, kitchen islands, or in foyers. Clusters of different filament styles can create a stunning centerpiece.
- Open-Socket Wall Sconces: Perfect for hallway, bathroom, or bedside lighting, where the bulb itself is the art.
- Table & Floor Lamps with Clear Globes: Any lamp with a transparent or glass shade becomes a showcase for the filament.
- Avoid: Enclosed fixtures (they overheat and obscure the filament), and spaces requiring ultra-bright, task-focused light like detailed workshop areas.
Balancing Ambiance with Energy Efficiency
While traditional incandescent filament bulbs are inefficient, modern options offer better performance. Making an informed choice here saves money and energy without sacrificing style.
The table below compares the core technologies available today:
| Type | How It Works | Efficiency & Life | Best For |
| LED Filament | LEDs arranged on a strip to mimic a filament's shape. | Very High (~80% less energy than incandescent). Lifespan: 15,000-25,000 hours. | Most applications. The practical choice for daily use and hard-to-reach fixtures. |
| Halogen Filament | An improved incandescent with halogen gas for a brighter filament. | Moderate. Lifespan: 2,000-4,000 hours. Gets very hot. | Purists wanting the perfect continuous filament glow and exact color rendering. |
| Vacuum / Classic Incandescent | Original Edison-style with a filament in a vacuum. | Low. Lifespan: 1,000-2,000 hours. High heat output. | Occasional or decorative use in well-ventilated fixtures where authenticity is paramount. |
Installation and Safety Considerations
Safe installation ensures your bulbs last and prevent hazards. Always turn off power at the circuit breaker before replacing a bulb. Handle bulbs with a clean, dry cloth; skin oils on glass can create hot spots and shorten the bulb's life, especially for halogen types. Ensure your fixture's maximum wattage rating is not exceeded—with LED filaments, this is rarely an issue due to their low wattage draw. Provide adequate clearance: filament bulbs, particularly halogens, need space around them as they generate significant heat. Do not let them come into contact with lampshades, wires, or flammable materials. For dimmable bulbs, use a compatible dimmer switch designed for LED or halogen loads to avoid flickering or buzzing.
Caring for Your Filament Bulbs
Dust them gently with a dry microfiber cloth when cool. Avoid using cleaning sprays directly on the bulb. The primary care is understanding their lifespan. An LED filament bulb may last over a decade with typical use, while a halogen may need replacing every few years. Planning for this avoids being left in the dark. When one in a matched set fails, consider if the others are near the end of their life to maintain a consistent look.

 English
English русский
русский