What Are LED Filament Bulbs?
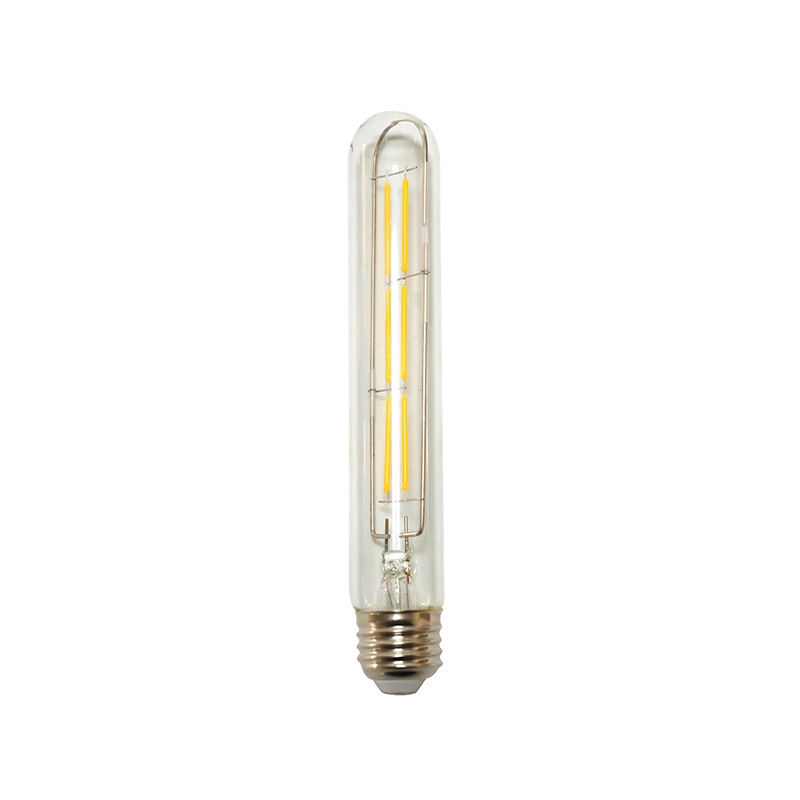
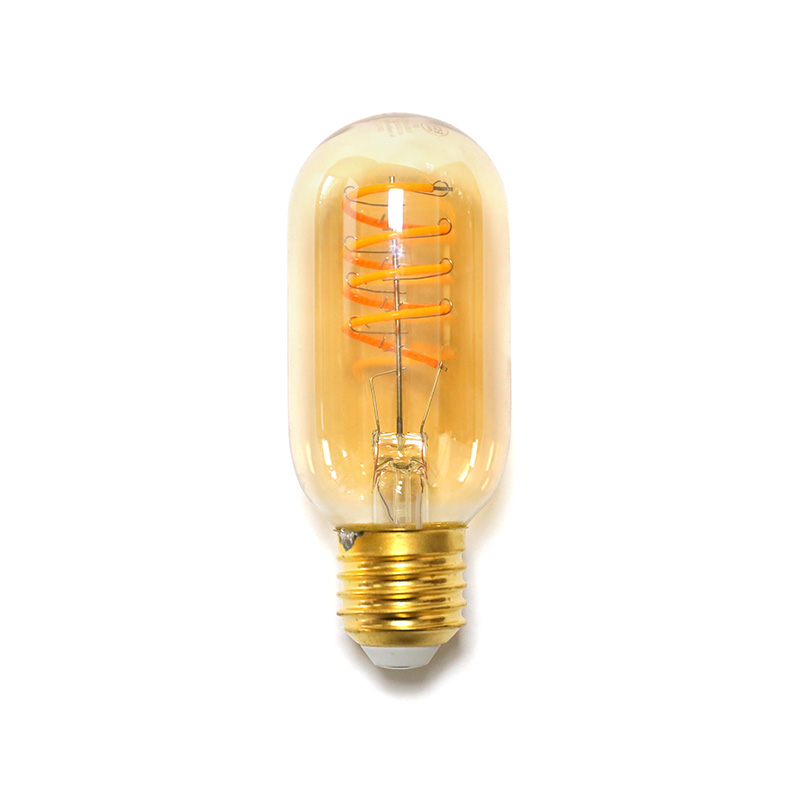
LED filament bulbs are a modern take on traditional incandescent bulbs that use light‑emitting diodes (LEDs) arranged in linear filament strands. Unlike conventional LEDs with opaque plastic diffusers, LED filament bulbs feature clear or lightly frosted glass and visible filaments that mimic the aesthetic of classic Edison bulbs. These bulbs combine vintage looks with cutting‑edge energy efficiency and long service life. Whether used for decorative fixtures, ambient lighting, or task lighting, LED filament bulbs are quickly replacing older technologies in homes, restaurants, offices, and industrial settings.
Core Advantages of LED Filament Bulbs
Energy Efficiency and Lower Operating Costs
LED filament bulbs use significantly less electrical power than traditional incandescent and halogen bulbs while delivering the same or higher light output. Standard incandescent bulbs convert less than 10% of electrical energy to visible light; most energy is wasted as heat. In contrast, LED filament bulbs convert a much higher percentage of energy into visible light, resulting in reduced electricity bills. For example, a 6‑8W LED filament bulb can produce as much light as a 60W incandescent bulb, saving up to 85% of energy usage.
Longevity and Reduced Maintenance
The average lifespan of LED filament bulbs ranges from 15,000 to 25,000 hours or more, depending on usage patterns and operating conditions. This far exceeds the 1,000–2,000 hours of traditional incandescent bulbs and even the 8,000–12,000 hours typical for compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs). Longer lifespan means fewer bulb replacements, lower maintenance labor costs in commercial buildings, and reduced waste over time.
Quality of Light and Aesthetic Appeal
LED filament bulbs offer excellent color rendering, often with a CRI (Color Rendering Index) of 80–95+, meaning they make colors appear natural and vibrant. Their transparent design and glowing filaments provide a warm, inviting look popular in hospitality and residential environments. Available in various color temperatures—from warm white (2700K) to cool white (5000K+)—these bulbs can suit many lighting needs.
Critical Specifications: How to Choose LED Filament Bulbs
Lumens: Measuring Light Output
Lumens indicate how much visible light a bulb produces. Higher lumens mean brighter light. When selecting an LED filament bulb, ignore wattage (which measures energy use, not brightness) and focus on lumens:
- 400–600 lumens: Suitable for small lamps, accent lighting, or night lights.
- 800–1100 lumens: Equivalent to a 60W incandescent—good for general room lighting.
- 1200–1600+ lumens: Equivalent to 75–100W incandescent bulbs—ideal for larger rooms or task lighting.
Color Temperature and Ambience
Color temperature, measured in Kelvins (K), determines how “warm” or “cool” the light appears. Consider these common ranges based on space usage:
- 2700K–3000K: Warm white—comfortable and cozy; ideal for living rooms and bedrooms.
- 3500K–4100K: Neutral white—good for kitchens, bathrooms, and offices.
- 5000K+: Cool white/daylight—best for garages, workspaces, and areas requiring high visibility.
Color Rendering Index (CRI)
CRI measures how accurately light displays colors compared to natural sunlight. Higher CRI values (above 80) are preferable in most indoor settings, and values of 90+ are recommended for areas where color discernment matters, such as retail, art studios, and food service.
Base Type and Fixture Compatibility
LED filament bulbs come with common bases like E26/E27 (standard screw base) and B22 bayonet base. Always check your fixture’s socket type. For specialty fixtures (e.g., candelabra or GU10), ensure you choose a compatible LED filament variant.
Comparative Table: LED Filament vs Other Bulb Types
| Feature | LED Filament Bulb | Incandescent Bulb | CFL Bulb |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Low | Medium |
| Lifespan (Hours) | 15,000–25,000+ | 1,000–2,000 | 8,000–12,000 |
| Warm Light Options | Yes | Yes | Limited |
| Instant On | Yes | Yes | Not Always |
| Contains Toxic Materials | No | No | Yes (Mercury) |
Practical Applications of LED Filament Bulbs
Residential Lighting Solutions
In homes, LED filament bulbs are ideal for fixtures where design matters: chandeliers, pendant lights, sconces, and exposed bulb fixtures. Their warm, inviting glow enhances living rooms, dining areas, and bedrooms. Because they draw little power and produce minimal heat, they are also safe for enclosed or decorative lamps.
Commercial & Retail Spaces
Retail businesses benefit from LED filament bulbs due to their excellent color rendering, which makes merchandise look true‑to‑life and appealing. Restaurants and cafés use them to create atmospheric lighting that’s both energy efficient and aesthetically pleasing. Long lifespans reduce maintenance costs in high‑ceiling areas where changing bulbs is labor‑intensive.
Outdoor and Decorative Lighting
Weather‑rated LED filament bulbs can be used in outdoor fixtures for porches, patios, and garden spaces. Their design suits string lights and decorative installations while drawing minimal power even when used in clusters. Always ensure outdoor bulbs have the proper IP rating for wet or damp locations.
Installation Tips and Best Practices
Proper installation extends bulb life and ensures optimal lighting performance. Follow these best practices when working with LED filament bulbs:
- Turn off the power at the switch or breaker before replacing or installing bulbs.
- Check the fixture’s maximum wattage rating; although LED filament bulbs use low wattage, physical size and heat considerations still matter.
- Avoid installing in fixtures not rated for enclosed bulbs unless the LED filament bulb packaging explicitly states it’s suitable for such use.
- For dimmable fixtures, ensure bulbs are labeled “dimmable” and compatible with your dimmer type to prevent flickering.
- Clean the bulb and socket contacts if replacing old bulbs to ensure solid electrical connection and reduce flicker or intermittent operation.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Flickering or Inconsistent Light
Flickering can be caused by incompatible dimmers, loose connections, or voltage fluctuations. First, ensure bulbs are properly seated in the socket. If flickering persists in dimmable circuits, check if the dimmer supports LED loads and replace it with an LED‑compatible model if needed.
Warm‑Up Delay or Reduced Brightness
Unlike older CFLs, LED filament bulbs should reach full brightness instantly. Reduced initial brightness may indicate a power delivery issue or bulb defect. Test the bulb in another fixture; if it performs normally, inspect wiring, switches, or smart controllers that may be limiting voltage.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
LED filament bulbs consume significantly less energy over their lifespan, reducing greenhouse gas emissions from power generation. Their long life decreases landfill waste and packaging. Unlike CFLs, LED bulbs do not contain mercury or other toxic elements, making disposal safer. Choosing LED filament bulbs aligns with broader sustainability goals for residential and commercial building upgrades.
By understanding key specifications, real‑world applications, and practical installation tips, you can make informed decisions that improve lighting quality, lower energy costs, and enhance the aesthetic value of your space using LED filament bulbs.

 English
English русский
русский